Configuring Secure Ciphers Suites and TLS
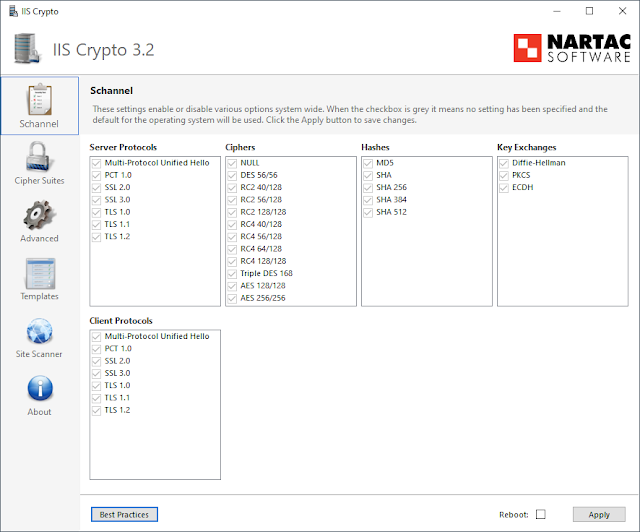
Hey everyone, today we're back on cipher suites. If you want a refresher of TLS and secure cipher suites overall, check out my previous post . There are many instances in which you'll need to edit cipher suites on a system -- compliance efforts, CIS benchmarks, or simply ensuring your system doesn't use insecure suites. There are a few ways to go about this and I'll detail two of them now: IIS Crypto and the Windows registry. IIS Crypto My favorite way of editing TLS versions and cipher suites is using IIS Crypto . IIS Crypto allows you to select your desired TLS/SSL version, cipher suites, and backup the registry, all with a few mouse clicks. Only downside is that it's Windows only (even the command line version). This is what IIS Crypto will look like on an unmodified Windows 10 system. Note the separate Server Protocols and Client Protocols sections. These are important to keep straight depending on what system is listening for connections and what system is


